The Samsung Galaxy Watch 4 is a fully-functional smartwatch powered by Google’s Wear OS. Besides the features we discussed in the FAQ, it has an exclusive Samsung BioActive Sensor. In this article, let’s see what BioActive Sensor is, how it works, and how to use it on the Galaxy Watch 4.
Related | 9 Things to Check When Buying a Smartwatch (2022)
What is the BioActive Sensor in Galaxy Watch?
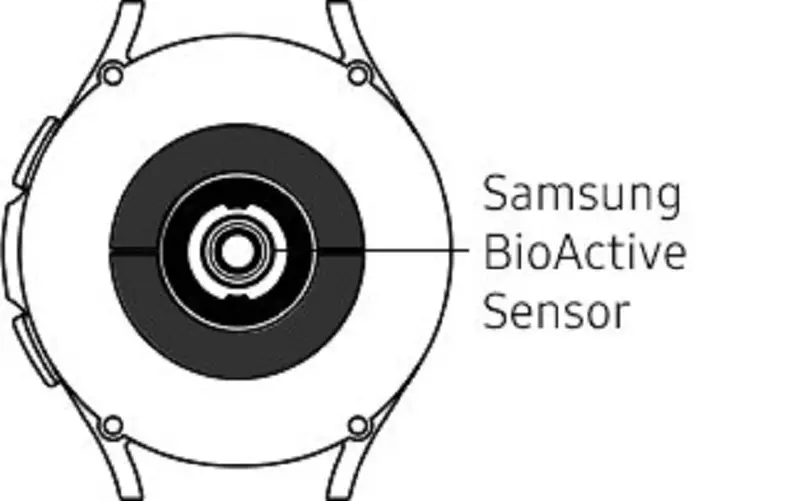
The BioActive sensor is Samsung’s official trademarked technology. This is a 3-in-1 sensor that uses a single chip to efficiently run three separate health sensors.
It includes an Optical Heart Rate sensor, Electrical Heart (ECG) sensor, and Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA) sensor. With the BioActive sensor, users can measure blood pressure, detect irregular heart rhythm (AFib), blood oxygen, and body composition.
How Does it Work?
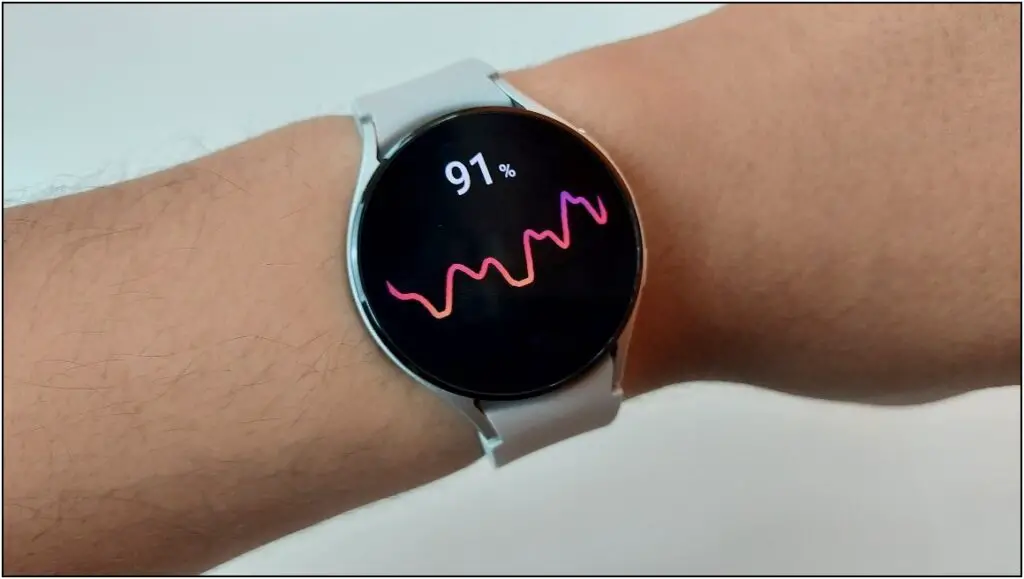

The Galaxy Watch 4 can measure your body composition data like body fat, fat mass, skeletal muscle, BMI, BMR, and body water. The BIA sensor embedded in the BioActive sensor uses current resistance to give these estimated body compositions.
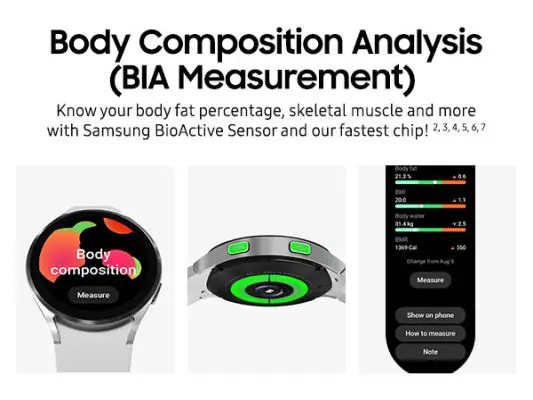
It requires a person to place their middle and ring finger on the side buttons while wearing the watch on the other hand. After that, the watch sends a low voltage current to the body. It forms a complete circuit that starts from the first finger and ends with another.
The different impedances like fat, muscle, and bone affect this current signal when passing throughout the body. After completing the circuit, it sends the collected information to Samsung’s own algorithms. And in about 15 seconds, it shows the data based on other individual factors like height, weight, and gender.
Before measuring the body composition data, the watch will ask for your weight and height to show more accurate results. It always gauges the current affected by signal with weight and height to show the final data.
What is BioActive Sensor Used For?
The BioActive sensor is a three-in-one chip that has all the sensors embedded inside. This sensor is used for your health-related data like heart rate, ECG, blood pressure, and body composition.
Let’s check the BioActive Sensor uses in detail:
Optical Heart Rate

The most common use of the BioActive sensor is the optical heart rate sensor which helps to measure heart rate. The Galaxy Watch 4 has built-in green LEDs and infrared lights to measure the heart rate along with the sensor. These LED lights are placed in between the BioActive Sensor chip.
Here’s more about the heart rate monitor in smartwatches and how it works.
Electrical Heart Detection (ECG)
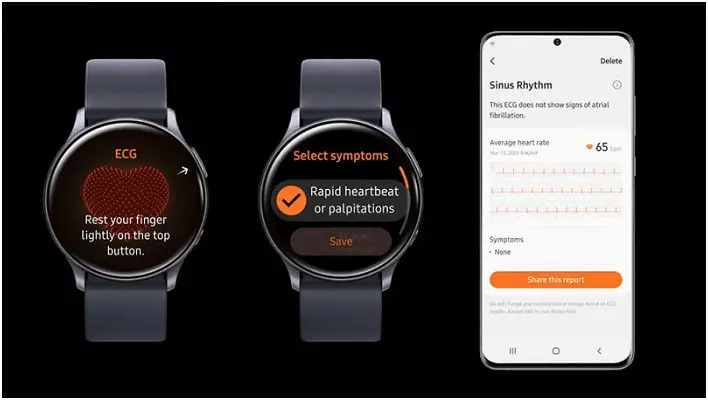
Another use of the BioActive sensor is electrical heart detection or ECG. The ECG sensor tracks heart health electrically and detects the heartbeat rhythm and alerts the user if the heart rhythm is irregular. It also warns the user about atrial fibrillation if any symptoms are found and help you to take treatment at right time.
The ECG sensor in the Galaxy Watch 4 is not FDA-approved in all countries, so you can’t use this feature if you are living in any of the ineligible countries. But you can still enable the ECG feature using a simple tweak.
Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis

The Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis or BIA is one of the main sensors that comes exclusively in the Galaxy Watch 4. This sensor helps the watch detect body composition data like body fat, body mass, skeletal muscle, etc.
The BIA sensor creates a current circuit throughout the body to receive signals from different impedances. Then, it collects all the data from over 2400 points and adjusts it according to weight and height.
At last, it shows the final results to you with the most accurate data. It takes a maximum of 15 seconds to complete the procedure and show the body composition data.
How to Use BioActive Sensor on Galaxy Watch 4?
As three major sensors are embedded in the BioActive sensor. Here’s how you can use each of the heart rate, ECG, and body composition features.
Measure Heart Rate
First of all, you can use the optical heart rate sensor to check your heart rate, as shown below:
Step 1: Swipe up on the watch’s home screen and select Samsung Health.


Step 2: Scroll down and select Heart rate. Click on the Measure button.
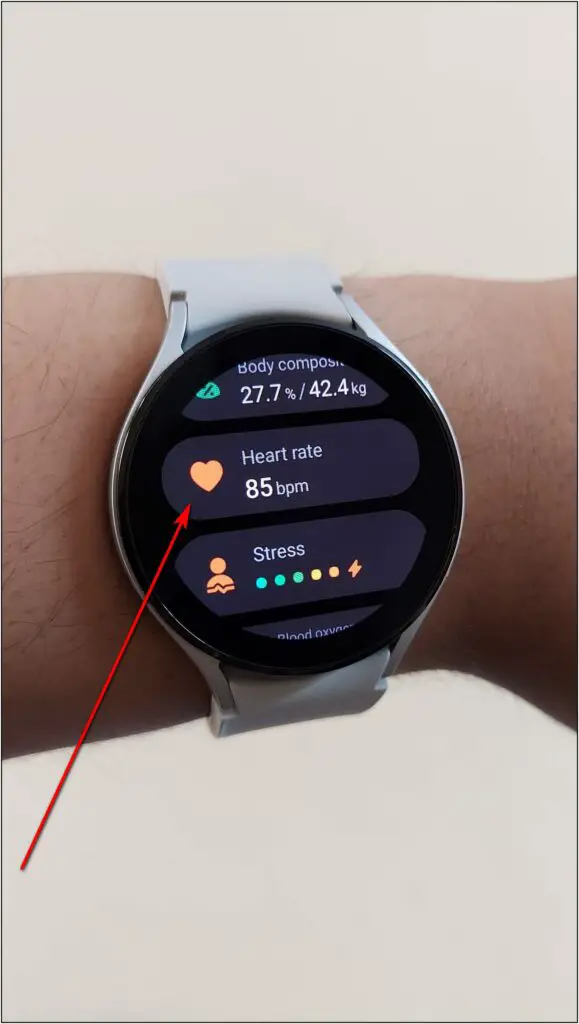
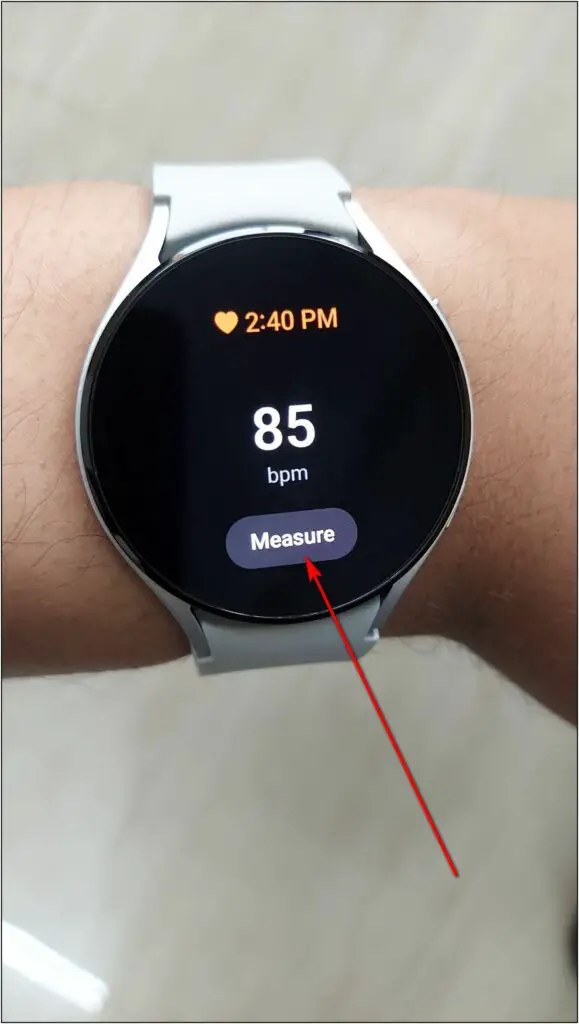
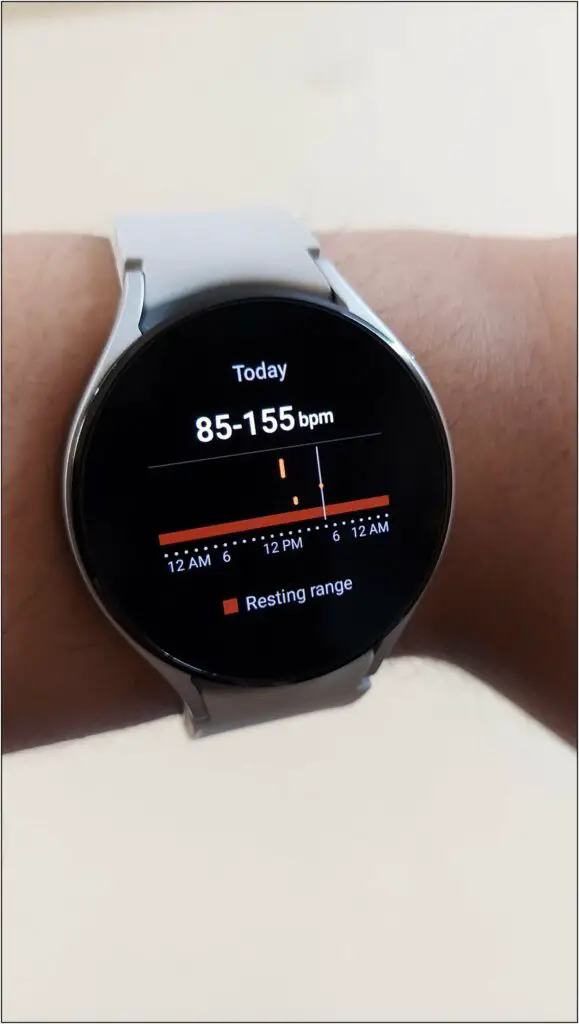
Now wait for a few seconds and it will show your heart rate with resting range as well on the screen.


Check ECG
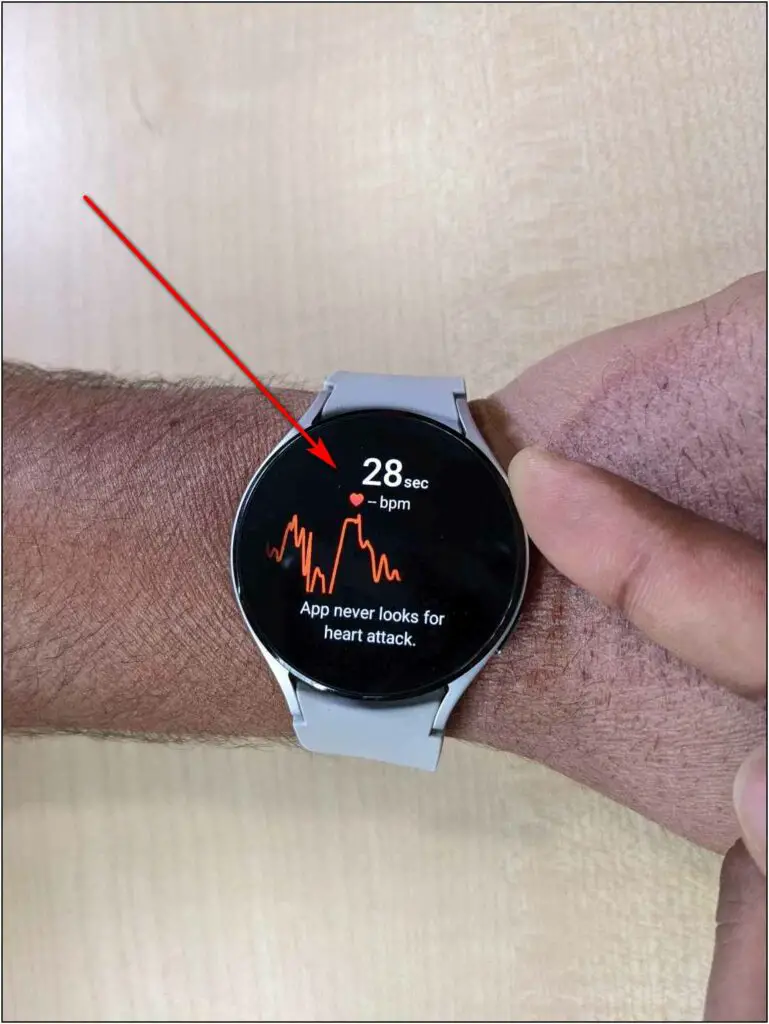
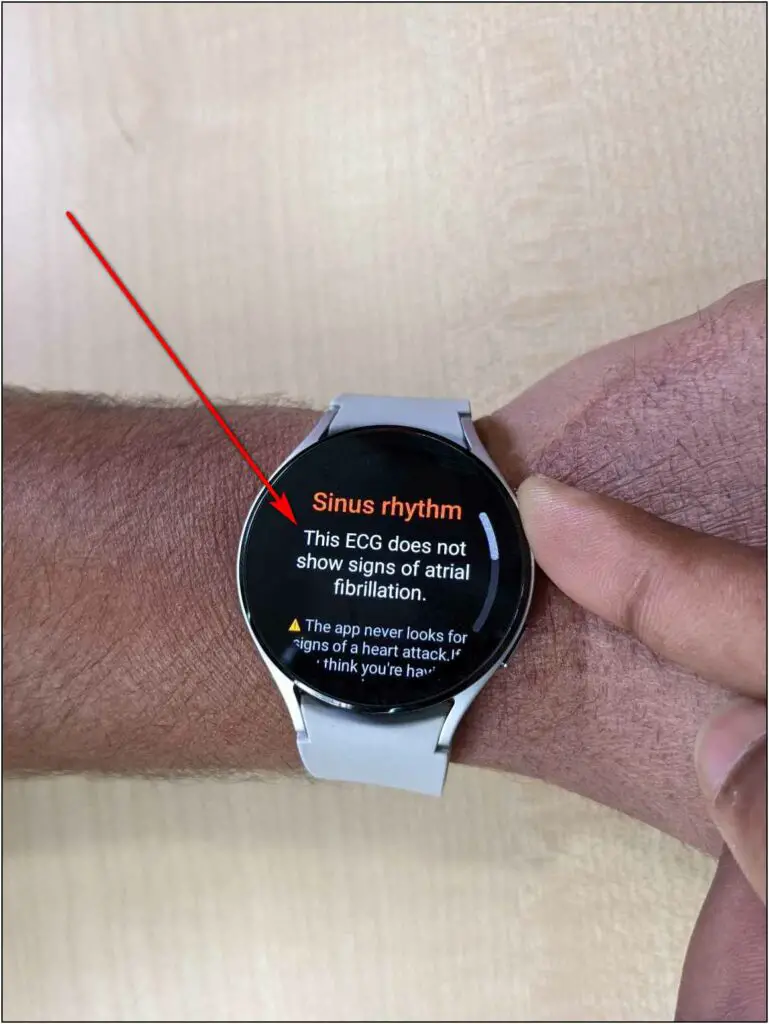



The second sensor is ECG which is available only in a few countries. But, you can still track your ECG anywhere around the world. All you need to do is open Samsung Health app on the watch, select ECG and follow the on-screen instructions.
Here’s a detailed guide to measure ECG using Galaxy Watch 4.
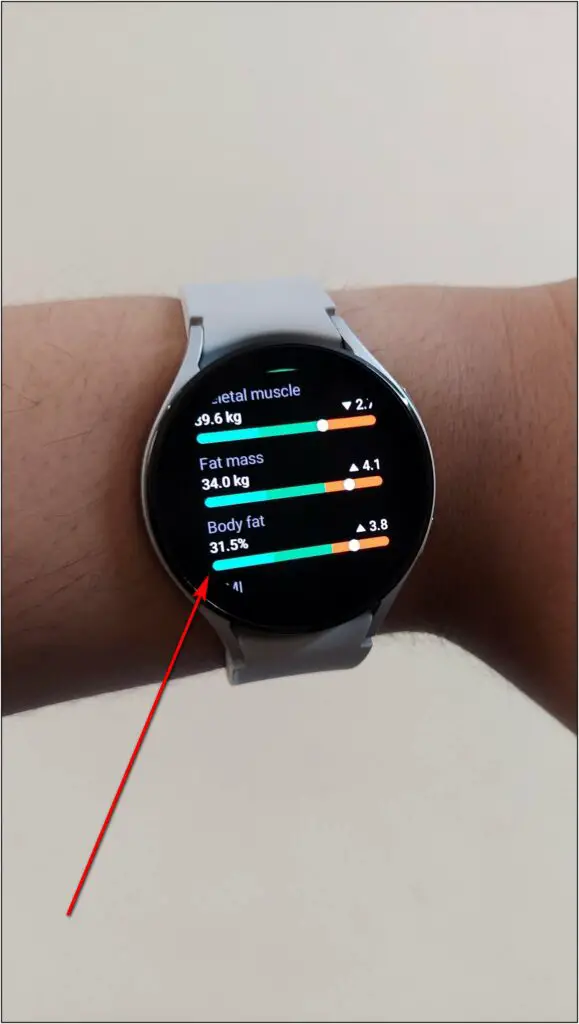
Find Body Composition
Next comes the BIA sensor that you can use to measure your body composition. Follow the steps mentioned below to use it:
Step 1: Swipe left on the Galaxy Watch home screen thrice.
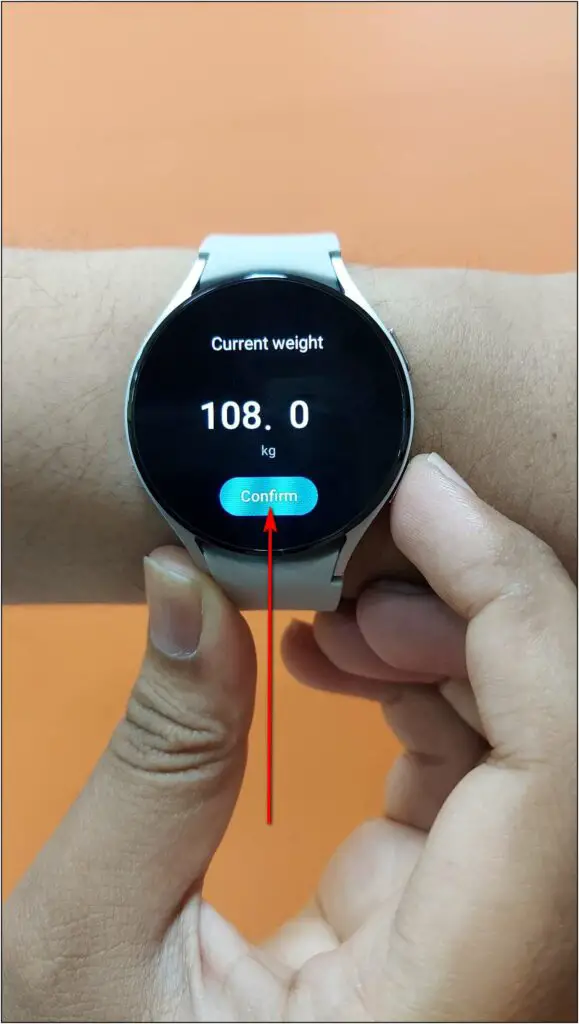
Step 2: Click on the Measure button and confirm your body weight.


Step 3: After that, place your middle finger on the upper key and ring finger on the lower key as shown in the instruction image.
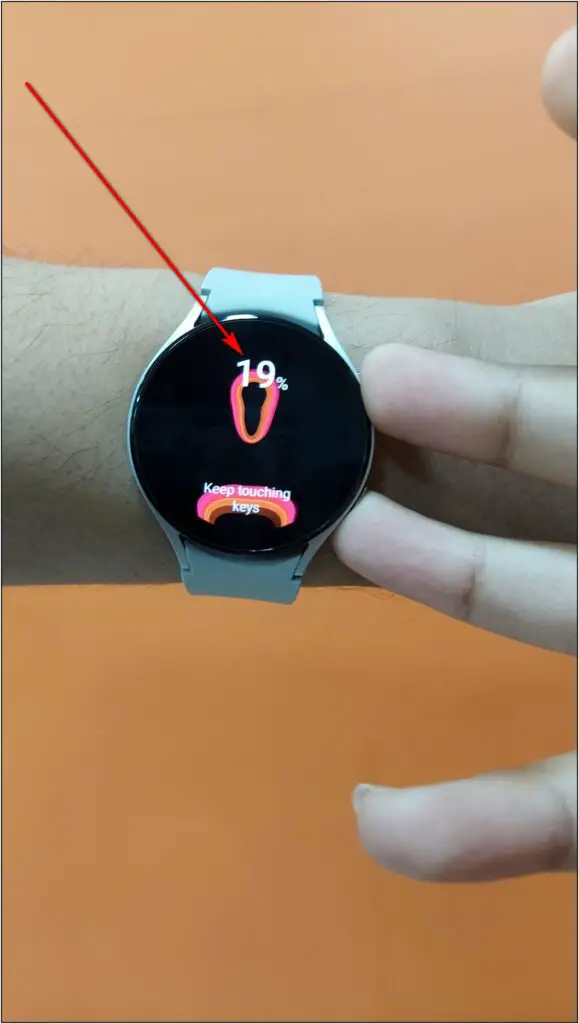


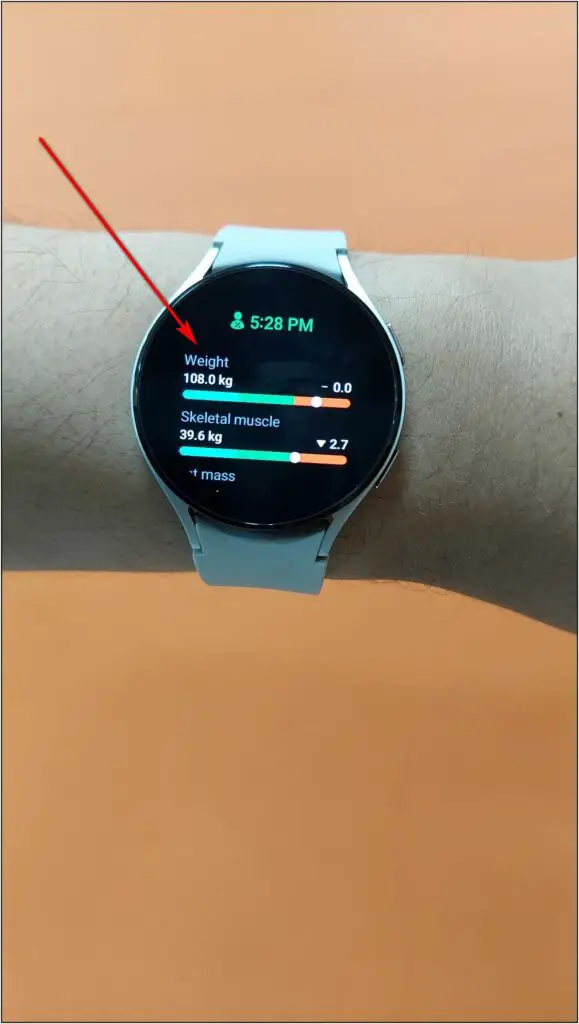
Now, wait for a few seconds until the measurement is completed to 100%. Once the measurement is done, it will show your body composition data.
How Accurate is the Galaxy Watch BioActive Sensor?
For all the health-related sensors in smart wearables, we know that the accuracy is not medical-grade. The technology is upgrading quickly but still, the experts suggest using medical equipment for any health-related data.
For the accuracy of the BioActive sensor in the Galaxy Watch 4, we have to see the accuracy of the BIA sensor mainly.

According to the tests done by Beebom, the Galaxy Watch 4’s BIA sensor is pretty accurate. They measured the body composition on Galaxy Watch 4 alongside Xiaomi’s Mi Body Composition Scale. The data was wiped on both devices and body composition data was measured twice for accurate results.
It was found that the body fat and fat mass metrics are about 5% higher in the Galaxy Watch 4 than the Mi Body Composition Scale. Also, the watch calculated the Basal metabolic rate as 1539 calories, whereas, the Mi scale calculated 1736 calories which are about 200 more than the Galaxy Watch 4’s data.
It can be concluded that Galaxy Watch 4’s BIA sensor is fairly accurate but not perfect for exact details. BIA sensor is a new technology that has entered the market with the Galaxy Watch 4. And Samsung has done a good job by implementing this on a watch.
However, you should not rely on it for medical diagnosis. Instead, use it periodically to get a general information about your body and health.
Wrapping Up
This was all about the BioActive Sensor in the Galaxy Watch 4, how it works, and the sensors involved. It’ll be interesting to see the next iteration of the technology on the rumored Galaxy Watch 5. I hope you learned something new in the article. Stay tuned with WearablesToUse for more informational content!



