In the last few years, there has been a meteoric rise in the advancement of consumer technology. We have access to technology more than ever. For the same reason, there is a constant worry about its health effects, at least in the long run. The primary concern is the radiation emitted, especially on devices like smartwatches, where one wears them for extended periods. Let’s understand smartwatch radiation and whether it is safe to wear.
What Are Radiations?
The crux of operations in any electronic device involves transmitting signals. The mode of energy transfer involved is called radiation – where electromagnetic signals are transmitted from one source to another. These signals carry a lot of important information, which is why they are important.
As we all know, much information is generated on a smartwatch, which also happens via transmitting and receiving signals. These signals are called electromagnetic waves. These waves do not need any medium to travel – unlike your sound waves and water waves (which are called mechanical waves).
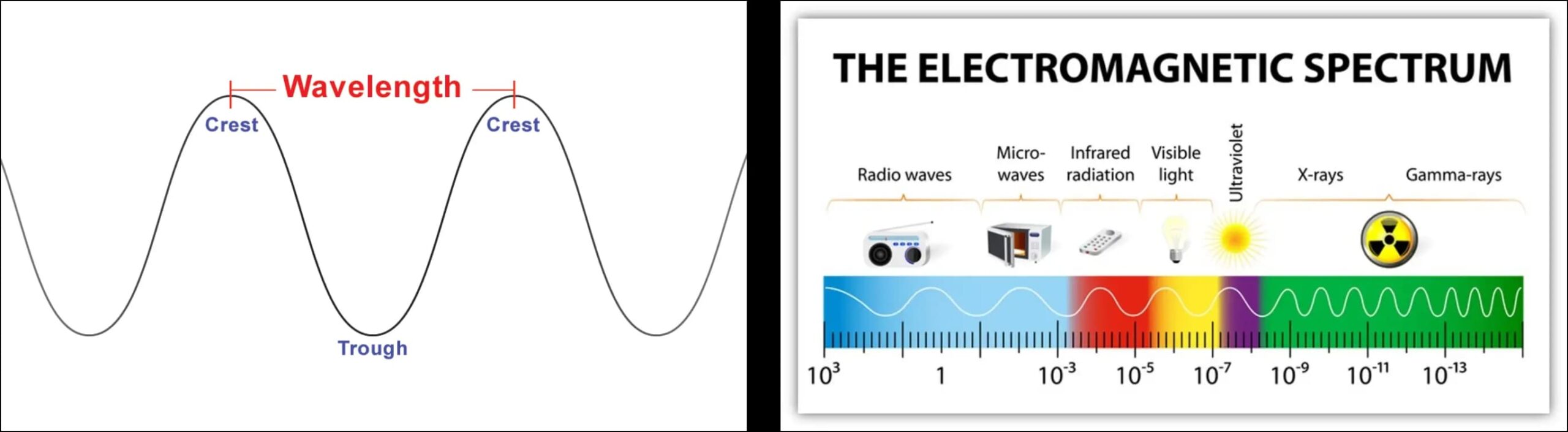
E.M. waves travel along with light, and different types of electromagnetic waves are segregated according to their wavelength. Now, wavelength is quite an important concept- imagine radiation as a ‘wave’; you now have two regions – a crest and a trough. It is a metric used to characterize a wave and its effects.
The distance between two crests is called a wavelength. Wavelength helps us understand the type of electromagnetic waves emitted and their frequencies – and in the case of smartwatches, you have three different types of waves – Radio waves, Microwaves, and Visible Light.
How Does a Smartwatch Emit Radiation?
Think about the basic activities that your smartwatch does. It uses Bluetooth and Wi-Fi signals to communicate with your smartphone.
These radiations emitted by WiFi are radiowaves, and Bluetooth operates via radiowaves and low-power microwaves. Then, you have all of your sensors. Take the heart rate sensor; for example, the LED lights emit infrared waves.
As mentioned, these waves are emitted as they carry signals – which help transfer information. The sole reason why different waves exist is that wavelengths and frequencies are related to the amount of energy that can be carried.
Different types of information transfer involve waves of different energies. Smartwatches, for starters, emit nonionizing radiations.
Understanding Ionizing vs. Non-Ionizing Radiation
“Oh, we are exposed to so many waves!” – we don’t blame you if this was your reaction after reading the previous section. Yes, some scientific terms can sound complex and can scare you. But here’s a rule of thumb – if there is any product out in the market by a renowned manufacturer sold on legitimate platforms, it is most likely safe and nonharmful to use. These devices must pass a few certifications to be sold to the general public. But if you were to get into the scientific reason, here’s what you need to know.
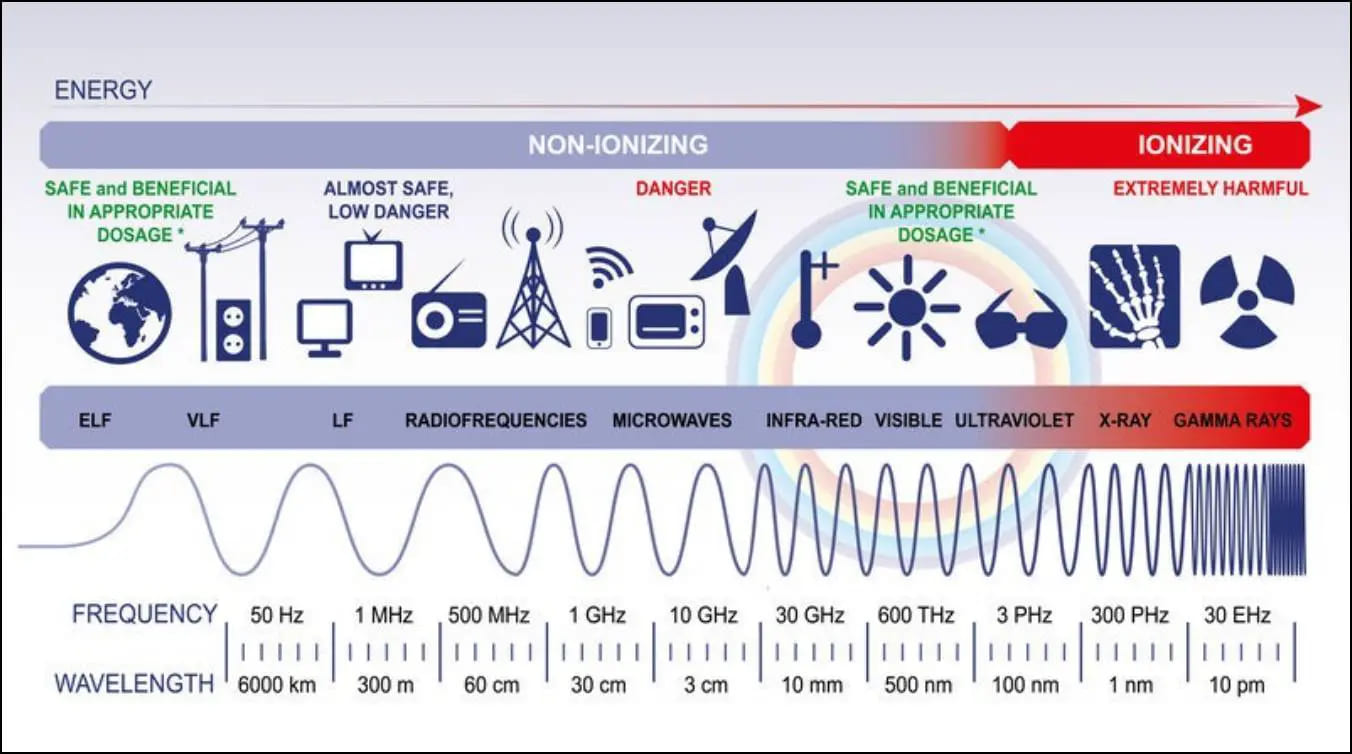
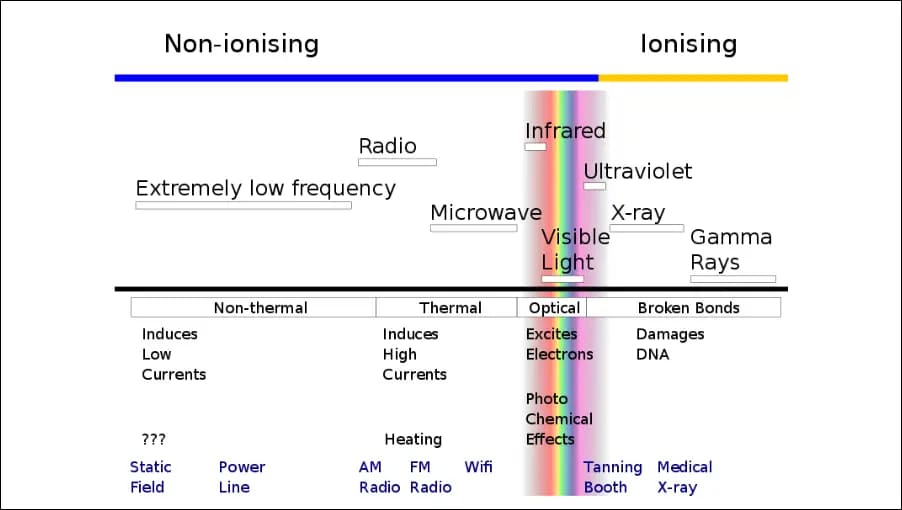
Radiation is of two different types – ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. Our area of interest here is non-ionizing radiation. As microwaves, radiowaves, and IR waves emitted by smartwatches come under non-ionizing radiation.
Radiation with enough energy to knock an electron out of an atom is ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation may alter the molecules that make up anything, including biological beings because chemistry is all about bonds created by electrons.
Changes to the chemistry of living things are significant because life is a chemical response. It could result in cancer.
Ionizing radiation, which includes UV light, X-rays, and gamma radiation, is anything with higher energy than visible light. Alpha and beta radiation from radioactive compounds is also a part of it.
It is radiation with insufficient energy to deprive atoms of their electrons and cannot change the chemical composition of objects. It can only heat objects and produce currents in conductors like antennas.
Everything less powerful than visible light is considered non-ionizing radiation, including infrared light and the whole radio spectrum, including microwave radiation utilized by microwave ovens, phones, WiFi, and Bluetooth signals.
Therefore, as mentioned earlier, these signals in the smartwatch come under non-ionizing radiations and are not practically harmful. So unless your smartwatch emits a lot of heat that can burn your skin – you are safe.
Mainly, the radio waves emitted are quantified as SAR values, and the SAR values for any device in the market have to be below the permissible limits prescribed by governing authorities, so even in that sense, you are safe.
Understanding SAR Values in Smartwatches
Even though these radiations aren’t harmful, you cannot completely rule them out. There is a parameter called SAR value attributed to every electronic device. SAR measures the rate of radiofrequency absorption by the body from the measured source. Even devices with the highest SAR value are nowhere near harmful.
These are plain numbers that result from the testing devices must undergo. These SAR values for all devices, including smartwatches, are prescribed by the FCC – the Federal Communications Commission of the United States.
In India and the US, the limit is 1.6 Watt/Kg. Smartwatches having a higher SAR value can not be sold in India.
You do not have to fear if you ever come across high SAR values. You might consider buying a smartwatch with a lower SAR value, thinking it might affect you less, but it really does not matter. The SAR values are accounted for using devices regularly – but it is a value observed under a worst-case scenario, and that too within a testing environment.
Firstly, there are low odds of you reaching this value in real life. And even if you do, it is still far from harmful to your body.
How to Check Radiation of Your Smartwatch?
As mentioned, the radiation of a smartwatch can be determined by its SAR value. And while it is mandated to be under safe limits, you can check the SAR value on your watch for peace of mind. Here’s how to determine the same:
- Manufacturer Website: Check if the brand has mentioned the smartwatch’s SAR value on the product page. Companies like Samsung and Apple have separate landing pages altogether to display RF exposure information.
- Smartwatch Box: Some brands mention the SAR values on the back of the watch’s retail packaging box.
- Smartwatch User Manual: You can also check the SAR value in the smartwatch user manual.
Can Smartwatches Ever Be Harmful?
Radiations are directly not harmful, as mentioned earlier. But if you are glued to your screens for long hours, you can end up with eye strain. Reading small text on a small display can amplify existing eye conditions. But these can’t be directly attributed to radiation.
If you wear your smartwatch all day, you might catch a skin infection if only your skin is sensitive. Most smartwatch brands use good quality, tested rubber for long usage.
Another way they can be harmful is there is always a sense of impending anxiousness about what you could see next when you have access to so much information on your wrist. A deluge of alerts on your wrist might be rather distracting as well. Additionally, health information is accessible on your wrist, and excessive use of these features may cause you to become too self-conscious and perhaps a little nervous about your health.
The bottom line is that unless these radiowaves generate so much heat that it increases your body temperature – No, they will not harm you.
Wrapping up
This is all you need to know about radiation in smartwatches and whether they affect you or not. We hope you found this article interesting. Stay tuned for more such guides to stay informed, and improve your knowledge of how wearables work.
You can also follow us for instant tech news at Google News or for tips and tricks, smartphones & gadgets reviews, join GadgetsToUse Telegram Group or for the latest review videos subscribe GadgetsToUse YouTube Channel.